Network flexibility of dedicated server grid: virtual rack and other tools
Choosing servers with powerful configurations is not always enough, especially for complex environments. Bandwidth and quality of internal network performance play an important role, as well as free network management in the case of leased infrastructure.
After all, too little capacity in the telecommunications area can be a bottleneck, so you won’t be able to use the full potential of the equipment. Dedicated servers operating in an extremely efficient network environment may be the solution to such problems.
Content:
Dedicated server lease service
High-performance environment based on dedicated servers
Network tools | Virtual rack (vRack) | Private VLANs | High-speed ports and their aggregation | Switch management
Network architecture and technologies | IP Fabric | VXLAN | Q-in-Q tunneling
Dedicated server lease service
Dedicated servers are more than just provided hardware with specific parameters. The service consists of the exclusive lease of servers (and other equipment, such as firewalls) of the chosen configuration, a place with appropriate environmental conditions in the data center, provision of uninterruptible power supply and servicing of equipment.
The service provider also provides an Internet connection with guaranteed bandwidth, usually equipped with protection against DDoS attacks. In addition, it is responsible for the internal network and provides network tools. The effective operation of the internal network depends largely on its architecture and the technologies used.
High-performance HA environment based on dedicated servers
Building a High Availability (HA) environment requires geo-redundancy first and foremost. So if you want to rely entirely on dedicated servers, find a provider that:
- Has two data centers, a minimum of several kilometers away from each other
- Provides dedicated server service at both locations
- Guarantees fast and secure communication between the centers.
The prerequisite for achieving exceptional performance in a server environment, in turn, is to choose a modernly designed platform, the so-called dedicated server grid. The grid’s architecture and equipment should include such technologies and tools that will enable you to manage a high-performance, preferably redundant network infrastructure.
Atman has a grid of dedicated servers that meets all the above conditions.
Network tools
Virtual rack (vRack)
A virtual rack, also sometimes called a private vRack network, is a solution that allows you to create a cluster(s) of servers from an unlimited number of machines. Physically, they can run in different server rooms or even different data centers. The effect is as if your dedicated servers were together in one rack, that is, on one LAN connected to the same switch.
Private VLANs
In Atman’s grid, you freely create multiple private virtual local area networks (VLANs), connecting your designated dedicated servers regardless of their location – even in different data centers. This applies both to devices inside and outside the vRack (virtual rack) network.
One of the advantages of using VLANs is the ability to dynamically transfer a public IP address within a single subnet.
High-speed ports and their aggregation
When choosing a server environment, pay attention to the bandwidth of network interfaces. In our grid, we provide you with 1 Gbps or 10 Gbps Ethernet ports. In addition, you can use the aggregation option, that is, at the logical level, combine several physical ports into one virtual (logical) port.
By using this feature, you not only increase the speed of communication, but also the reliability of access to a given dedicated server. If one of the group of aggregated ports starts having problems or fails, the others will provide you with uninterrupted connectivity to the server.
Switch management
Moreover, in the architecture of our new grid, each dedicated server is connected to two independent network switches, whose roles you define yourself, according to your current needs. This means that instead of using one internal network and one link to the Internet, you can assign both switches the same task and use them to build two internal networks or set up two channels for Internet access.
The redundancy of the network infrastructure and the free management of it by the user significantly supports the creation of high-performance computing environments in Atman’s grid.
Network architecture and technologies
In designing the network in the new grid, we decided to throw aside the traditional hierarchical three-tier topology and implement IP Fabric / VXLAN technologies. As a result, the grid architecture of Atman Dedicated Servers:
- Supports high data packet forwarding performance and low latency
- Allows the creation of a virtually unlimited number of VLANs
- Facilitates traffic flow management
- Allows IP addresses to be transferred between different VLANs
- Minimizes the risk of network connection failures.
IP Fabric
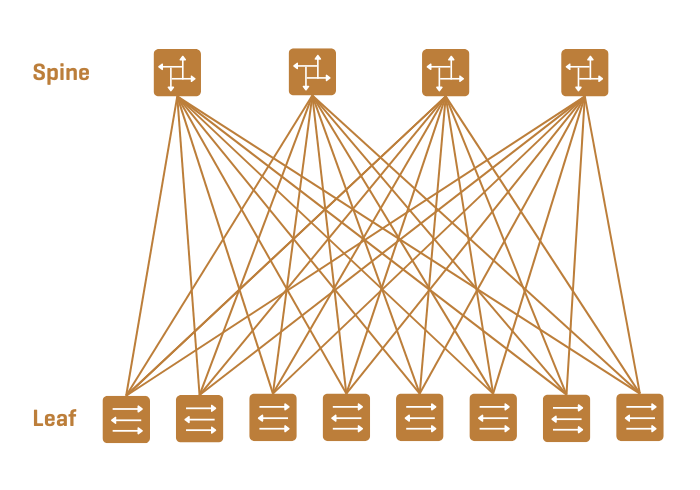
The IP Fabric architecture we chose – an underlay IP network – is based on a two-tier topology called spine-leaf, which provides significant acceleration of east-west (horizontal) communication, i.e. between devices physically dispersed in the data center.
In the topology we used, each rack switch (leaf switch) is directly connected to all grid switches (backbone switch, or spine switch). As a result, communication between any two servers requires a maximum of three network devices.
VXLAN
To provide even faster east-west communication in our grid, and to lift the limitation on the number of VLANs that can be built in a single network, we implemented VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) technology.
VXLAN is among the most popular overlay technologies, which are logical networks built on top of physical (underlay) networks to virtualize network resources.
By overlaying VXLAN on the IP Fabric network, we can connect leaf switches directly to each other using virtual tunnels. When tunneling, VXLAN uses MAC-in-UDP packet encapsulation.
In addition, the advantage of this technology is the enormous potential for network separation. The VXLAN Network Identifier (VNI) field is 24 bits long, so as many as 16 million network segments with individual VNIs can be isolated. In comparison, the VLAN ID field, the VNI counterpart, is half as long, and this means that with VLAN technology, only 4096 virtual LANs can be isolated within a single network.
Q-in-Q tunneling
Our grid’s architecture also supports IEEE 802.1 Q-in-Q tunneling, or Q-in-Q for short.
Q-in-Q tunneling among others:
- Allows you to separate several virtual networks within a master VLAN, for example, assigned by Atman
- Allows us to combine your VLANs into a single so-called service VLAN, for example, to achieve additional separation of your traffic within a single data center or to allow your traffic to flow between different data center locations.
Q-in-Q tunneling is a way of creating layer 2 Ethernet connections by adding one more layer of 802.1Q tags to VLAN frames. The leaf switch of the server sending the traffic inserts the appropriate service VLAN (S-VLAN) tag before the client’s 802.1Q VLAN tag. Only the S-VLAN tag is used in the propagation. The target switch gets rid of the external tagging and forwards the traffic to the addressed server.
Modern grid of Atman Dedicated Servers
Check out the high-tech, tool-enabled network architecture that will allow you as a user of the Atman Dedicated Servers service to manage the communications of your machines as if they were in a single rack. Minimize latency and maximize the performance of your server environment!




 The website uses cookies as described in our
The website uses cookies as described in our 